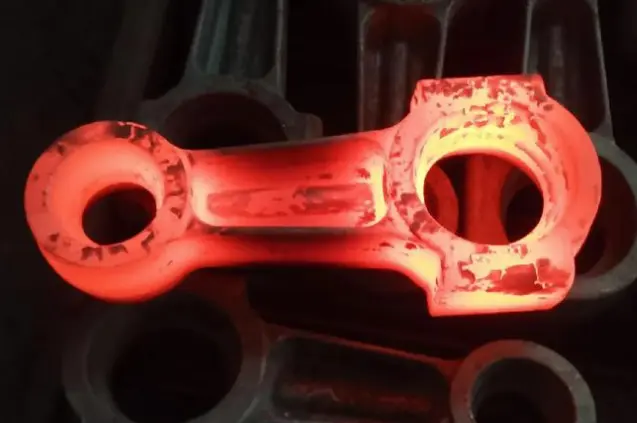
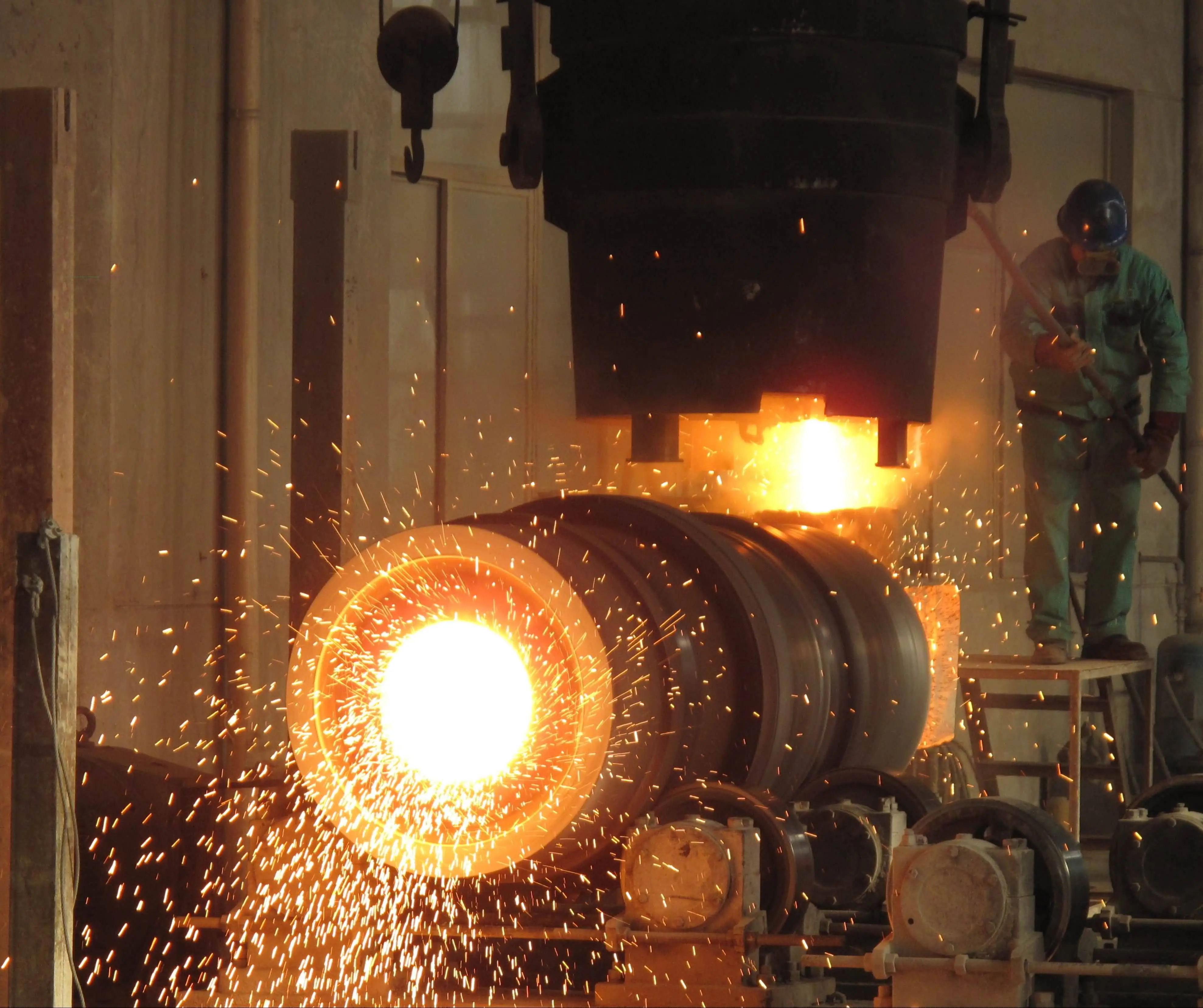
The Best Surface Treatments for Cold Forged Parts
Cold forging is a widely used manufacturing process that produces high-strength, precision parts with excellent surface finishes. However, to enhance the performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal of cold forged components, various surface treatments are often applied. These treatments can improve wear resistance, corrosion protection, and overall part functionality. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the best surface treatments for cold forged parts, discussing their benefits, applications, and how they contribute to the longevity and effectiveness of manufactured components. From traditional methods to cutting-edge technologies, we'll delve into the most effective surface treatments that can elevate the quality of Cold Forging Parts across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Understanding these treatments is crucial for manufacturers and engineers looking to optimize their cold forging processes and produce superior quality parts.
What are the most effective surface treatments for improving the durability of cold forged parts?
Electroplating
Cold forged items can have their surface treated with electroplating to make them more resistant to corrosion and increase their longevity. The cold forged component is covered with a thin layer of metal by use of an electric current during this procedure. Zinc, nickel, chromium, and copper are some of the most common metals used in electroplating. There are a number of benefits to electroplating cold forged components. Particularly in hostile settings, it offers superior protection against corrosion. The plated layer not only increases the part's lifespan but also makes it more resistant to wear. Electroplating also gives cold forged items a glossy, appealing surface, which can enhance their visual appeal. Because of the high aesthetic and functional standards set by the automotive and aerospace sectors, this treatment is ideal for cold forged components utilized in these fields. Adaptable to a wide range of cold forged component uses, the method can be fine-tuned to produce components with desired thicknesses and qualities.
Powder Coating
When it comes to cold forged items, powder coating is a great surface treatment since it adds both durability and aesthetic variety. A hard, protective layer is formed by adding a dry powder to the surface of the cold forged component and then curing it under heat. Powder coating is perfect for Cold Forging Parts that are subjected to rough environments because it offers great protection against chipping, scratching, and fading. In addition, it protects the components from corrosive substances and has great chemical resistance. Because it does not use solvents and generates very little waste, powder coating is an eco-friendly option for cold forged products. You may customize it to match your individual design requirements with the vast choice of colors and finishes available. Protective and aesthetically pleasing powder coating is ideal for cold forged components utilized in outdoor applications, automobile parts, and consumer items.
Anodizing
Cold forged and aluminum alloy parts can be greatly enhanced in appearance by anodizing. An oxide layer is electrochemically applied to the metal's surface, which provides a long-lasting protective coating. Anodizing cold forged aluminum components has several potential uses. It makes the parts more resistant to corrosion, which means they last longer and work better in rough environments. In addition to increasing the cold forged components' longevity, the anodized layer increases their resistance to wear. Aside from giving the components a vibrant new hue, anodizing also improves their functionality and looks great. Adjusting the oxide layer thickness allows you to fine-tune this approach to your precise requirements. Aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics are just a few examples of industries that frequently use anodized cold forged parts due to their lightweight and durable nature. There are new applications for adhesives and paints since the components get stickier as they pass through it.
How does heat treatment affect the surface properties of cold forged parts?
Carburizing
When cold forged components, especially those composed of low-carbon steel, undergo carburizing, a heat treatment procedure, their surface qualities are considerably improved. To do this, the components are heated in a carbon-rich atmosphere, which allows the carbon to permeate the metal's surface. There are a number of benefits to carburizing cold forged components. It produces a surface that is hard and resistant to wear while keeping the core strong and ductile. Gears and shafts, which endure tremendous strain and wear, benefit greatly from the combination. Components subjected to continual stress are well-suited to cold forged parts due to their outstanding fatigue resistance. The exceptional fatigue resistance of cold forged parts makes them ideal for components that endure continuous stress. This quality is improved by the carburized layer. The surface's resistance to deformation under heavy loads can also be enhanced by carburizing. Parts that are cold forged and utilized in gearboxes for automobiles, factories, and farms benefit greatly from this treatment. The depth of the carburized layer can be controlled, allowing for customization based on specific application requirements.
Nitriding
Cold forged components can have their surface qualities significantly enhanced by nitriding, another heat treatment procedure. Usually performed at lower temperatures than carburizing, this procedure entails diffusing nitrogen into the metal's surface layer. Nitriding provides superior surface hardness and wear resistance for Cold Forging Parts. Because of its extraordinary hardness, the nitrided layer offers superior resistance to wear caused by abrasive materials. Stainless steels and tool steels are among the many materials that can be nitridized, in contrast to carburizing. The treated surface is also made more corrosion resistant by the treatment. Parts that necessitate great dimensional stability can benefit from nitriding for cold forged components because it produces little distortion. Many hydraulic systems, cutting tools, and automobile engines make use of nitrided cold forged components. The treatment can enhance the fatigue strength of the parts while also boosting their overall durability and performance in demanding applications.
Induction Hardening
Cold forged components can have their surface characteristics improved by induction hardening, one of numerous heat treatment processes available. Using electromagnetic induction, the surface layer of the component is heated quickly and cooled down afterwards. There are various benefits to using induction hardening on cold forged components. A robust and wear-resistant exterior and a soft and resilient interior are the end results. Ideal candidates for this combination would be components that require great resistance to surface stress and wear without sacrificing overall toughness. It is now possible to achieve targeted hardening on complicated cold forged components with the help of finely regulated induction hardening. This is very effective for components whose stress requirements vary over their surface areas. Ideal for mass-producing cold forged components, this procedure is quick and uses little energy. Machine tools, industrial machinery, and automobile drive train parts are typical applications for induction hardened cold forged components. The components are strengthened against cyclic stresses by increasing their fatigue strength through treatment.
What are the latest advancements in surface coating technologies for cold forged parts?
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
An sophisticated surface coating process known as Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) has becoming increasingly popular for improving cold forged components. The cold forged part is coated with a thin layer of a solid material that has been vaporized in a vacuum. PVD coatings are known for their remarkable hardness, resistance to wear, and low friction characteristics. When exceptional performance and durability are paramount, PVD coatings offer cold forged items an advantage over conventional surface treatments. Precision cold forged components can have coatings as thin as a few micrometers while still retaining their dimensional correctness. In addition to providing long-lasting protection, PVD has great substrate adherence. Cutting tools, aircraft components, and high-performance automobile parts are some of the many applications for cold forged parts that benefit greatly from this technology. The adaptability of cold forged parts is further enhanced by the ability to apply numerous layers with varied qualities. This opens the door to tailor-made coatings that are tailored to meet the demands of individual applications.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Another state-of-the-art surface coating method that has worked well for cold forged components is chemical vapor deposition (CVD). The procedure begins with heating the substrate, and then the required coating is produced by reacting or decomposing volatile precursors on the surface. Chemical vapour deposition coatings provide chemical inertness, wear resistance, and extraordinary hardness to Cold Forging Parts. Intricate cold forged components benefit greatly from this method since it can provide homogeneous coatings even on complicated geometries. The superior adherence of CVD coatings to substrates guarantees their longevity throughout time. Cold forged items used in high-temperature applications greatly benefit from this method, as many CVD coatings maintain their characteristics even when heated. The ability to deposit a varied range of materials, including ceramics and diamond-like carbon, opens up new possibilities for increasing the performance of cold forged components. Cold forged components that have been CVD coated are utilized in cutting tools, aircraft, and high-performance engines.
Thermal Spray Coatings
As a novel surface treatment method, thermal spray coating shows promise for cold forged products. The cold forged component is coated with a protective coating by spraying molten or semi-molten materials onto its surface. Coatings applied by thermal spray have a special set of advantages when applied to cold forged components. They have great wear resistance in addition to being heat and corrosion resistant. Metals, ceramics, and polymers are just a few of the many materials that can be used with this method because of its adaptability. This adaptability allows for the customization of coating qualities to match the specific requirements of cold forged products. The ability to apply thermal spray coatings in thicker layers than other coating procedures makes them ideal for components that are subjected to severe conditions or wear and tear. This process can extend the life of cold forged components, restore damaged surfaces, and handle large parts. The aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery industries all make use of cold forged parts that have been thermal spray coated.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the selection of appropriate surface treatments for cold forged parts is crucial for enhancing their performance, durability, and longevity. From traditional methods like electroplating and powder coating to advanced technologies such as PVD and CVD, each treatment offers unique benefits tailored to specific applications. Heat treatments like carburizing and nitriding provide excellent wear resistance and surface hardness, while newer coating technologies offer unprecedented levels of protection and customization. As manufacturing technologies continue to evolve, it's essential for engineers and manufacturers to stay informed about these surface treatment options to optimize the quality and functionality of Cold Forging Parts across various industries.
Choose Welong for Expert Customized Metal Parts Solutions
Shaanxi Welong Int'l Supply Chain Mgt Co.,Ltd, established in 2001, is a leading provider of customized metal parts for diverse industries. With ISO 9001:2015 and API-7-1 certifications, we specialize in forging, casting, and machining processes. Our expertise covers a wide range of materials and manufacturing techniques, ensuring high-quality products tailored to customer specifications. We offer comprehensive support from design to delivery, including quality control and logistics management. With a global customer base spanning over 100 clients in 20 years, we strive to be a frontrunner in international supply chain management and China's intelligent manufacturing. Our commitment to reasonable pricing, product excellence, and exceptional service makes us an ideal partner for your manufacturing needs. For more information, contact us at info@welongpost.com.
FAQ
Q: What is the most common surface treatment for cold forged steel parts?
A: Electroplating is one of the most common surface treatments for cold forged steel parts, offering excellent corrosion resistance and improved appearance.
Q: Can anodizing be applied to all cold forged parts?
A: Anodizing is primarily used for aluminum and its alloys. It's not suitable for steel or other non-aluminum cold forged parts.
Q: How does powder coating compare to wet paint for cold forged parts?
A: Powder coating generally provides a more durable and uniform finish compared to wet paint, with better resistance to chipping and scratching.
Q: Are PVD coatings suitable for large cold forged parts?
A: While PVD coatings are excellent for many applications, they can be challenging and expensive to apply to very large parts due to the vacuum chamber size limitations.
Q: Can surface treatments affect the dimensional accuracy of cold forged parts?
A: Some treatments, like thick coatings, can slightly alter dimensions. However, processes like PVD and anodizing have minimal impact on part dimensions.
References
1. Smith, J. (2020). Advanced Surface Treatments for Cold Forged Components. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 29(8), 4912-4925.
2. Johnson, A. & Lee, S. (2019). Comparative Analysis of Coating Technologies for Cold Forged Parts. Surface and Coatings Technology, 378, 125-137.
3. Brown, R. (2021). Innovations in Heat Treatment Processes for Cold Forged Steel. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 52(6), 2345-2360.
4. Garcia, M. et al. (2018). Electroplating Techniques for Enhanced Durability of Cold Forged Components. Plating and Surface Finishing, 105(3), 22-30.
5. Thompson, L. (2022). PVD and CVD Coatings: Next-Generation Solutions for Cold Forged Parts. Thin Solid Films, 740, 139-151.
6. Wilson, K. & Davis, T. (2020). Thermal Spray Coatings: Advancing the Performance of Cold Forged Industrial Components. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 29(7), 1567-1582.

Share your inquiry, get the quotation accordingly!

China WELONG- Your Reliable Partner in Metal Solutions

