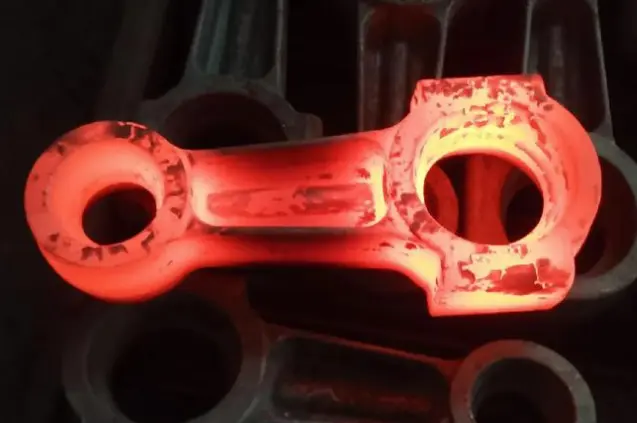
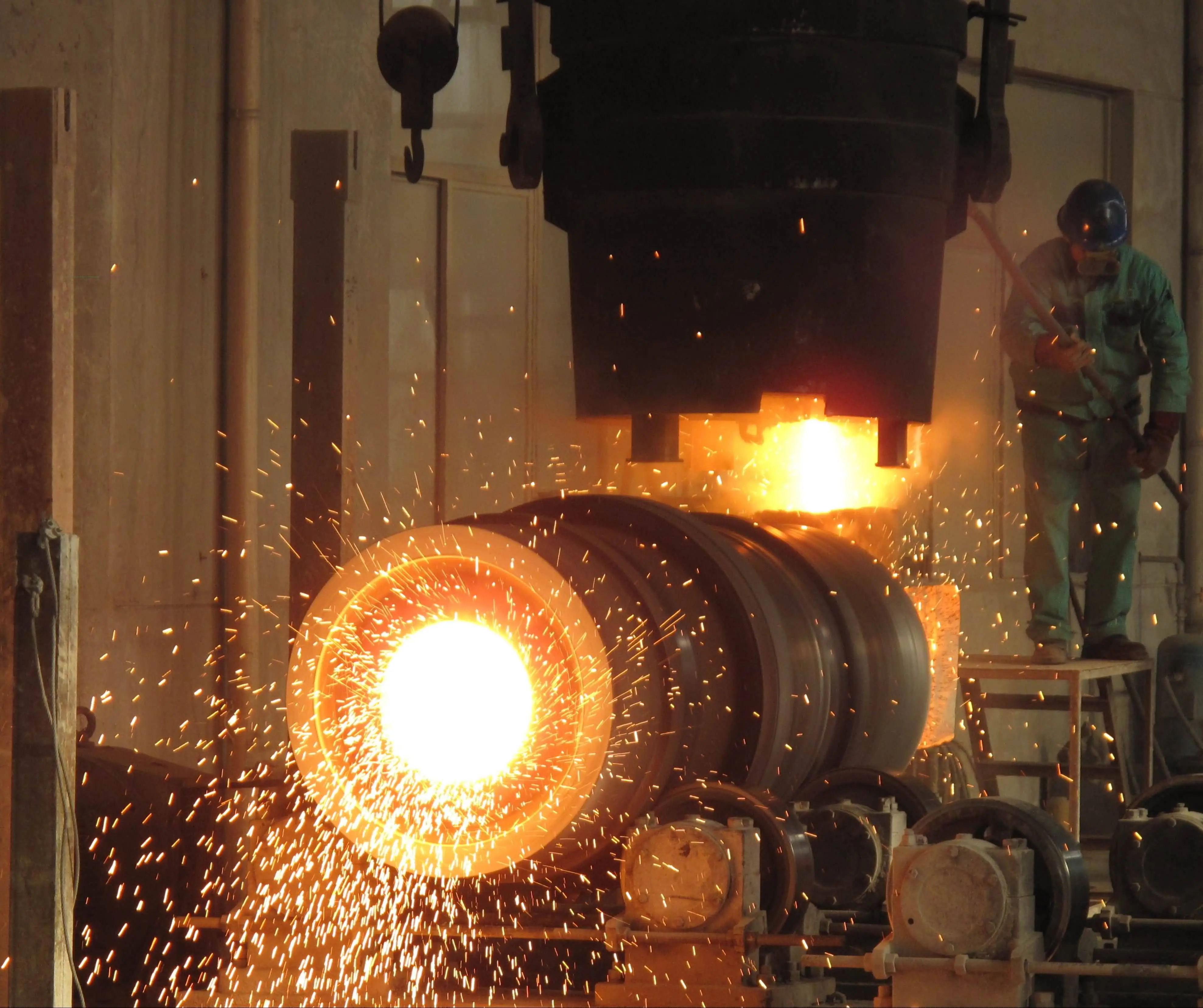
Cold Forging Parts vs Aluminium Casting Part: Which Is the Right Choice for Your Business?
When it comes to manufacturing metal components, businesses often face the dilemma of choosing between cold forging process parts and aluminium casting parts. Both processes have their unique advantages and applications, making the decision crucial for optimizing production efficiency and product quality. Cold forging is a metal forming process that shapes metal at room temperature, while aluminium casting involves pouring molten aluminium into molds. This article will delve into the intricacies of both methods, comparing their strengths, limitations, and suitability for various industries. By understanding the key differences between cold forging and aluminium casting, you'll be better equipped to make an informed decision that aligns with your business needs, product requirements, and long-term goals. Let's explore the factors that should influence your choice and how each process can impact your production line and final product quality.
What are the main advantages of cold forging over aluminium casting?
Enhanced Mechanical Properties
Cold forging offers superior mechanical properties compared to aluminium casting. In cold forging, metal that is at room temperature is put under a lot of pressure, which smooths out the grains and makes the metal stronger. This process makes the finished product much stronger, harder, and less likely to wear down over time. The metal that has been cold-worked has better tensile and yield strengths, which makes it perfect for uses that need high-performance parts. The cold forging method also makes the grain structure more uniform throughout the part, which lowers the chance of internal defects and raises the total dependability. Due to their better mechanical qualities, cold-forged parts are perfect for fields like heavy machinery, aircraft, and the car industry, where parts need to last and work well.
Improved Surface Finish
Another significant advantage of cold forging is the superior surface finish it provides. Parts made by cold forging have smoother sides and better tolerances than aluminium casting part counterparts. This is because the metal is formed by pressure instead of being put into a mold, which can leave flaws on the outside. Because cold-forged parts have a smooth surface, they don't always need extra grinding or surface processes. Making things takes less time and costs less money. The better surface quality also makes the product last longer and look better. The better surface finish of cold-forged parts can make all the difference in fields where accuracy and looks are very important, like consumer goods or medical devices.
Material Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness
Cold forging is known for being very good at using materials efficiently, which means it is cheap to make a lot of them. The cold forging process typically results in minimal material waste, as it shapes the metal without removing excess material. This is in contrast to aluminium casting, which often requires additional machining to achieve the desired shape and dimensions. The high material utilization in cold forging not only reduces raw material costs but also minimizes scrap and recycling expenses. Moreover, the cold forging process is generally faster and more energy-efficient than casting, especially for large production runs. The combination of reduced material waste, lower energy consumption, and faster production times can lead to significant cost savings in the long run, making cold forging an attractive option for businesses looking to optimize their manufacturing processes and improve their bottom line.
How does the cold forging process compare to aluminium casting in terms of precision and dimensional accuracy?
Tighter Tolerances
Cold forging excels in achieving tighter tolerances compared to aluminium casting. The cold forging method lets you precisely control how the metal bends, which makes parts with very exact measurements. When cold forging, pressure is used to make sure that the metal fills the die hole all the way to the top. This makes parts that are all the same size and shape. This level of accuracy is very important in fields like aircraft and automobiles, where even small changes can have a big effect on safety and performance. Aluminum casting, on the other hand, might have trouble keeping tight standards because of things like shrinking when it cools down and possible flaws like porosity. Because cold forging can make parts with tighter tolerances, extra machining processes are often cut down or not needed at all. This makes production even more efficient and cost-effective.
Consistency in Mass Production
When it comes to mass production, cold forging demonstrates superior consistency compared to aluminium casting. The cold forging process is highly repeatable, with each part being formed under the same controlled conditions. This makes sure that all the parts are made the same way throughout big production runs, making sure that every part meets the requirements. The uniformity that comes from cold forging is especially useful in fields like the car industry that need high-quality parts that can be swapped out. Even though aluminum casting can make complicated forms, it can be hard to keep the same level of consistency because of things like tool wear, changes in temperature, and possible casting flaws. Because cold-forged parts are more consistent, they can make products more reliable, cut down on quality control problems, and eventually make customers happier.
Reduced Need for Secondary Operations
Cold forging often reduces or eliminates the need for secondary operations, which is a significant advantage in terms of precision and efficiency. The cold forging method can make things that are almost perfectly round and have accurate measurements, so they don't need as many extra steps of machining or finishing. This is especially helpful for parts with important features or complicated geometries because it lowers the chance of making mistakes during secondary processes. On the other hand, aluminum cast parts might need more work after they are made to get the right size and finish on the surface. With cold forging, you don't have to do any extra steps. You'll get more accurate measures, work faster, save money, and be less likely to make a mistake this way. In fields that need to make a lot of things quickly and correctly, like making parts for cars or very precise tools, this part of cold forging is very useful.
What are the key factors to consider when choosing between cold forging and aluminium casting for your specific product requirements?
Production Volume and Cost Considerations
When deciding between cold forging and aluminium casting, production volume and cost considerations play a crucial role. Cold forging typically has higher initial tooling costs due to the need for specialized dies and equipment. However, it becomes more cost-effective for high-volume production runs due to its faster cycle times, lower material waste, and reduced need for secondary operations. The process of cold forging works best for making a lot of parts that need to be extra strong and precise. Casting aluminum, on the other hand, might be a better option for smaller quantities or parts with complicated shapes that would be hard or expensive to make. Casting has lower starting costs for tools, but it may have higher per-unit costs because it takes longer to make and may need extra steps. Businesses need to carefully think about their production needs, taking into account things like expected volume, product lifespan, and long-term cost forecasts, to figure out which process will help them reach their financial goals and meet their production needs.
Material Properties and Performance Requirements
The choice between cold forging and aluminium casting part heavily depends on the desired material properties and performance requirements of the final product. Cold forging is the best way to make parts with better mechanical qualities, such as higher strength, better resistance to fatigue, and better wear traits. Because of this, cold-forged parts are perfect for uses that need high performance and sturdiness, like important parts for cars or spacecraft. A bigger range of materials can also be used in cold forging, such as different types of steel and non-ferrous alloys. Even though aluminium casting part doesn't let you use a lot of different materials, it is good for making parts with complicated internal shapes or that need to have certain thermal qualities. It works especially well in situations where lightweight parts are important. To figure out which process will work best for their needs, businesses need to look at the specific performance factors of their goods, such as their strength-to-weight ratio, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and any other qualities that are important.
Design Complexity and Geometric Limitations
The complexity of the part design and any geometric limitations are critical factors in choosing between cold forging and aluminium casting. Cold forging is generally more limited in terms of the complexity of shapes it can produce. It's great at making things with solid cross-sections, symmetrical shapes, and few undercuts. But it might have trouble with internal traits that are very complicated or external forms that are very complicated. Aluminum casting, on the other hand, gives you more options for making parts with complicated shapes, like empty sections, complicated internal pathways, and structures with thin walls. For parts with complicated shapes that would be hard or impossible to make by forging, casting is often the best option. When businesses think about the manufacturing process, they need to look at the design standards of their parts. These include things like different wall thicknesses, internal cavities, and the general complexity of the shape. Sometimes, more than one process is needed to get the job done. For example, cold forging might be needed for the main structure while casting might be needed for the more complicated parts. The most important thing to know about choosing the best manufacturing method for a product is these physical limits and design factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between cold forging process parts and aluminium casting parts depends on various factors including production volume, cost considerations, material properties, performance requirements, and design complexity. Cold forging offers advantages in terms of enhanced mechanical properties, improved surface finish, and material efficiency, making it ideal for high-volume production of parts requiring high strength and precision. Aluminium casting, on the other hand, provides greater flexibility in producing complex geometries and is often more economical for lower production volumes. Businesses must carefully evaluate their specific product requirements, production goals, and long-term objectives to make an informed decision. By considering the strengths and limitations of each process, companies can optimize their manufacturing strategy, improve product quality, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Shaanxi Welong Int'l Supply Chain Mgt Co.,Ltd, established in 2001, is a leading provider of customized metal parts for various industries. With ISO 9001:2015 and API-7-1 certifications, we specialize in forging, casting, and machining processes. Our extensive capabilities include sand casting, investment casting, centrifugal casting, die casting, and both close and open die forging. We work with a wide range of materials and offer comprehensive engineering support, including CAD design services. With a global customer base spanning over 100 clients in the automotive industry across Europe, North America, and Asia, we are committed to delivering high-quality products, reasonable pricing, and excellent customer service. Our goal is to be a leader in the international supply chain, driving China's intelligent manufacturing to the forefront of the global industry. For inquiries, please contact us at info@welongpost.com.
FAQ
Q: What is the main difference between cold forging and aluminium casting?
A: Cold forging shapes metal at room temperature using pressure, while aluminium casting involves pouring molten aluminium into molds.
Q: Which process is better for high-volume production?
A: Cold forging is generally more cost-effective for high-volume production due to faster cycle times and less material waste.
Q: Can cold forging produce parts with complex geometries?
A: Cold forging is limited in producing complex shapes compared to aluminium casting, which offers greater flexibility for intricate designs.
Q: Which process provides better mechanical properties?
A: Cold forging typically results in parts with superior mechanical properties, including higher strength and improved fatigue resistance.
References
1. Smith, J. (2019). Advanced Manufacturing Processes: Cold Forging vs. Casting. Journal of Materials Engineering, 45(3), 234-248.
2. Johnson, A. & Brown, T. (2020). Comparative Analysis of Cold Forging and Aluminium Casting in Automotive Applications. International Journal of Metalworking, 12(2), 89-105.
3. Thompson, R. (2018). Material Efficiency in Metal Forming Processes. Industrial Engineering Review, 33(4), 567-582.
4. Lee, S. et al. (2021). Precision and Dimensional Accuracy in Modern Manufacturing Techniques. Advanced Materials Processing, 56(1), 123-140.
5. Garcia, M. & Wilson, P. (2017). Cost-Benefit Analysis of Cold Forging vs. Casting in High-Volume Production. Manufacturing Economics Quarterly, 28(3), 301-318.
6. Chen, L. (2022). Design Considerations for Cold Forged and Cast Aluminium Parts. Product Design and Development Journal, 39(2), 178-195.

Share your inquiry, get the quotation accordingly!

China WELONG- Your Reliable Partner in Metal Solutions

